Element of Art Produced When a Wavelength of Light Strikes and Object and Reflects Back to the Eyes
What is Color?

Color consists of three properties:
- Hue — The name given to a color, such as red, yellowish, blue, purple, greenish, orange, etc.
- Intensity (or saturation) — The purity or dullness of a color. A color's purity is determined by whether information technology has been mixed with another hue and, if so, to what extent. The virtually vibrant colors are those correct from the tube. Colors that have been combined with diverse hues are idea to be less intense. To reduce the intensity of a color, at that place are two options:
1) Mix the color with gray.
2) Mix the color with its complement. - Value — The lightness or darkness of a colour. Calculation white or black to a hue changes its value. A "tint" is created when white is added, while a "shade" is made when black is added.
Using color effectively in creating art involves understanding iii basic areas: the color wheel, color value, and color schemes (or color harmony.)
The Color Wheel

-
The primary colors are red, yellow, and blue. These hues are as spaced apart on the colour wheel. There are only three primary colors, and they are the virtually basic colors on the wheel. They can simply be made from natural pigments and cannot exist fabricated by mixing other hues. These three primary colors tin exist blended to create any other color on the color wheel.
-
Secondary colorsare orangish, green, and purple (or violet). These colors are created by mixing equal parts of any two primary colors.
- Red + yellow = orange
- Yellowish + blue = light-green
- Bluish + red = violet (regal)
- Third colorsare ruddy-purple, red-orange, blue-greenish, blue-majestic, yellow-greenish, and yellow-orange. At that place are six tertiary colors, and they are the result of mixing equal parts of a primary color with a secondary color. The proper way to refer to third colors is by list the primary colour first and so the secondary color. Tertiary colors are called by their two-discussion name.
-
Reddish + violet (purple) = red-violet (red-purple)
- Red + orange = ruby-orange
- Bluish + greenish = blue-green
- Bluish + violet (purple) = blue-violet (blue-purple)
- Yellow + orange = yellow-orange
- Yellowish + dark-green = yellow-greenish
-
Colour Values
Color also has value. A color's value is a measurement that describes how calorie-free or dark it is. It is defined by the color's proximity to white. For instance, lighter colors such equally xanthous will have lighter values than darker colors like navy bluish.
A proficient way to meet the departure in the values of colors is to look at the greyscale. White is the lightest value, while black is the darkest. Middle grayness is the value halfway between these two extremes.
A color'due south value can be changed past simply adding white or black to information technology. When you add white to a hue, yous go a lighter value. "Tints" are the lighter values. When you add black to a color, the value darkens, creating a "shade" of that color. Meet the instance below.
Color Temperature
The temperature of color is how we perceive a particular color, either warm or cool. Warm colors range from red to xanthous on the colour wheel, whereas absurd colors range from blue to green and violet. Each temperature takes upwards one-half of the color bike (come across images below). Somewhere in the green and violet spectrums, the temperature changes between warm and absurd.
The characteristics of warm and cool colors include:
Warm Colors
-
-
are made with red, orange, or yellow, and combinations of them
- tend to experience warm, reminding us of heat and sunshine
- tend to accelerate into the foreground, i.eastward., come toward the viewer
- may experience more energetic, attention-grabbing, and aggressive
-
Cool Colors
-
-
are made with blue, green, or violet, and combinations of them
- tend to experience cool, reminding us of water and sky
- tend to recede into the background, i.e., move away from the viewer
- are more calming and soothing
-
Neutral Colors
Neutral colors practise not appear on the color chart and are neither warm nor cool. They are chosen neutral because they lack color and are derived by mixing equal parts of color opposites (i.due east., cherry-red + greenish, bluish + orange, or yellow + purple), resulting in drab-looking grays.
Black and white are also considered neutral considering they are neither warm nor cool and do non change color.
This lesson on "Basic Fine art Element — Color" continues in part 2, where colour harmony is discussed.
Take The Quiz
Examination your cognition of color theory by taking this simple online exam.
Your Next Art Lesson
If you enjoyed this lesson, be certain to check out another one in this serial.
The Basic Elements of Art (Introduction)
Bones Fine art Element — Color, Function i — You are here.
Basic Art Element — Color, Part 2
Bones Art Element — Line
Bones Art Element — Space
Bones Art Element — Texture
Basic Art Element — Value
More Art Lessons
Good Design Principle: An Introduction
Good Pattern Principle: Rest
Skilful Design Principle: Contrast
Practiced Design Principle: Emphasis
Good Pattern Principle: Movement
Proficient Design Principle: Proportion
Good Design Principle: Space
Skilful Design Principle: Visual Economic system
Good Design Principle: Unity
Have a question?
If you accept a question about this painting, please contact us, and we'll be happy to answer any of your questions.
Thanks for reading this art lesson!
Feel free to share this with your friends.
UPDATED: 25 June 2021
Savor this page? Please share it. Thanks!
Source: http://teresabernardart.com/basic-art-element-color/
 The primary colors are red, yellow, and blue. These hues are as spaced apart on the colour wheel. There are only three primary colors, and they are the virtually basic colors on the wheel. They can simply be made from natural pigments and cannot exist fabricated by mixing other hues. These three primary colors tin exist blended to create any other color on the color wheel.
The primary colors are red, yellow, and blue. These hues are as spaced apart on the colour wheel. There are only three primary colors, and they are the virtually basic colors on the wheel. They can simply be made from natural pigments and cannot exist fabricated by mixing other hues. These three primary colors tin exist blended to create any other color on the color wheel. Secondary colorsare orangish, green, and purple (or violet). These colors are created by mixing equal parts of any two primary colors.
Secondary colorsare orangish, green, and purple (or violet). These colors are created by mixing equal parts of any two primary colors. 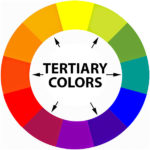 Reddish + violet (purple) = red-violet (red-purple)
Reddish + violet (purple) = red-violet (red-purple)
 are made with blue, green, or violet, and combinations of them
are made with blue, green, or violet, and combinations of them
0 Response to "Element of Art Produced When a Wavelength of Light Strikes and Object and Reflects Back to the Eyes"
Post a Comment